Hysteroscopy
Minimally Invasive
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive diagnostic and surgical procedure that is essential for examining the inside of the uterus. This procedure is typically performed using a hysteroscope, a thin, lighted tube that is inserted into the vagina to examine the cervix and inside of the uterus.
Common Reasons for Performing Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is utilized for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Here are some of the primary reasons for its use:Diagnosis of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Hysteroscopy can help determine the cause of irregular bleeding by allowing the doctor to look directly at the uterine lining.Investigation of Repeated Miscarriages: For women experiencing multiple miscarriages, hysteroscopy can be used to identify any uterine anomalies that could be contributing to the miscarriages.Location and Retrieval of Intrauterine Devices (IUDs): If an IUD is misplaced or embedded in the uterine wall, hysteroscopy can assist in locating and removing the IUD.Implantation of Permanent Birth Control: Some forms of permanent birth control involve placing devices inside the fallopian tubes to block them, which can be done using hysteroscopy.Removal of Adhesions: Known as Asherman’s syndrome, these are bands of scar tissue that can form in the uterus and can be removed via hysteroscopy.
Benefits of Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy offers several benefits over other types of surgical procedures:Less Invasive: Unlike traditional surgery, hysteroscopy does not require incisions, which typically results in quicker recovery and less pain.Performed Under Local or General Anesthesia: Depending on the complexity, hysteroscopy can be performed with local or general anesthesia. Many simple procedures can even be done in a doctor’s office.Short Recovery Time: Most patients can return to their normal activities within a day or two after a non-complicated hysteroscopic procedure.Diagnostic and Therapeutic: Hysteroscopy can be used not only to diagnose a condition but also to immediately address the identified issues, such as removing polyps or fibroids.
Potential Risks and Complications
Although hysteroscopy is generally safe, like any medical procedure, it carries potential risks. These may include:InfectionHeavy BleedingInjury to the Cervix, Uterus, or Surrounding OrgansReactions to AnesthesiaPatients are advised to discuss the potential risks and benefits of hysteroscopy with their healthcare provider.
Preparing for Hysteroscopy
Preparation for hysteroscopy may involve several steps to ensure safety and effectiveness:Pre-procedure Medications: Depending on the specific needs, pre-medication may be prescribed to dilate the cervix before the procedure.Fasting: Patients may need to fast for several hours prior to the procedure if general anesthesia is used.Arranging for Transportation: Patients should plan for someone to drive them home after the procedure if sedation or general anesthesia is used.Hysteroscopy is a valuable tool in gynecology that aids in diagnosing and treating various uterine conditions. By providing a direct view of the uterine cavity, it offers a clear advantage in the precision management of gynecological health.
Laparoscopy
Minimally Invasive
Laparoscopy, often referred to as “minimally invasive surgery,” is a surgical technique in which operations are performed far from their location through small incisions elsewhere in the body. In this procedure, a laparoscope, a thin instrument with a high-intensity light and a high-resolution camera at the front, is inserted into the abdominal wall through a small incision. The camera sends images to a video monitor, giving the surgeon a clear view of the internal organs.
Common Uses of Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is used for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Here are some of the most common applications:Diagnostic: It helps diagnose a range of abdominal and pelvic conditions, often when non-invasive methods cannot provide enough information.Surgical: Common laparoscopic surgeries include removal of the gallbladder, appendix, adhesions, hernia repairs, hysterectomies, and weight loss surgeries.
Benefits of Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, including:Reduced Recovery Time: Patients typically recover faster due to smaller incisions.Less Pain Post-Operation: The minimally invasive approach results in less postoperative pain and consequently, reduced dependency on pain medications.Decreased Risk of Infection: Smaller incisions minimize the exposure of internal organs to external contaminants, which can decrease the risk of postoperative infections.Less Scarring: Smaller incisions also result in less noticeable scars.
Potential Risks and Complications
Despite its benefits, laparoscopy can involve risks such as:Infection, bleeding, and hernias at the incision sitesDamage to organs near the surgical siteRisks associated with anesthesiaPatients should discuss these potential risks with their healthcare provider to make an informed decision.
Preparing for Laparoscopy
Preparation for laparoscopy may include:Preoperative Tests: Blood tests, imaging studies, and other examinations to ensure safety during surgery.Fasting: Patients may be required to fast for a specific period before the surgery to avoid complications during anesthesia.Medication Adjustments: Informing the surgeon about current medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to avoid potential interactions.
Recovery and Aftercare
Post-laparoscopy, patients may experience discomfort such as pain at the incision sites, abdominal bloating, and shoulder pain due to the CO2 used during surgery. Recovery advice may include:Activity: Light walking is encouraged to prevent blood clots.Diet: Initially, a light diet may be recommended to resume normal gastrointestinal function.Wound Care: Instructions on how to care for the incision sites to prevent infection.Laparoscopy is a valuable surgical method that has revolutionized many procedures, significantly reducing the burden of surgery on patients. It is crucial for patients to follow their surgeon’s advice on recovery and attend follow-up appointments to ensure the best outcomes.
Hysterectomy
A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the uterus, offering a permanent solution for various gynecological issues. This procedure can alleviate chronic pain, bleeding, and other symptoms associated with conditions like fibroids, endometriosis, uterine prolapse, or cancer.
Types of Hysterectomies Performed at Alexandria Women’s Center
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy (TAH)This traditional form of hysterectomy involves removing the uterus and cervix through an incision in the lower abdomen. It is generally recommended when access to the abdomen is needed, such as in the case of large fibroids or when disease is widespread.Total Vaginal Hysterectomy (TVH)In this procedure, the uterus is removed through the vagina, eliminating the need for an external incision. It is often preferred for conditions like uterine prolapse, where the uterus descends into the vaginal canal.Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy (TLH)TLH involves the removal of the uterus and cervix using a laparoscope, which is inserted through small incisions in the abdomen. This method reduces recovery time and scarring and is suitable for a variety of gynecological issues.Laparoscopic Assisted Vaginal Hysterectomy (LAVH)LAVH combines laparoscopic and vaginal approaches. It starts with laparoscopy to detach the uterus and is completed with the vaginal removal of the uterus. This method is beneficial when better visualization of abdominal organs is required.Laparoscopic Supracervical Hysterectomy (LSH)In LSH, only the uterus is removed, leaving the cervix intact. This option might be chosen to reduce surgical risks and preserve pelvic structural integrity, potentially offering a quicker recovery and less post-operative pain.
Benefits of Minimally Invasive Hysterectomy
Minimally invasive techniques (TLH, LAVH, LSH) generally offer several advantages over traditional abdominal surgery, including:Shorter hospital staysFaster recovery timesLess post-operative painReduced scarringLower risk of infection
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any surgery, hysterectomies carry risks such as:InfectionBleedingInjury to adjacent organs such as the bladder or intestinesRisks associated with anesthesia
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery from a hysterectomy varies depending on the type of surgery performed and the individual’s health. Typical recovery involves:Pain managementAvoiding lifting heavy objects for several weeksRestrictions on driving and sexual activity until clearance from a healthcare providerPatients should follow specific aftercare instructions provided by their surgeons to ensure the best recovery outcomes.The decision to undergo a hysterectomy at Alexandria Women’s Center will be guided by factors specific to each patient’s condition and health profile. Our team is dedicated to providing personalized care, discussing all available options, and supporting our patients through recovery.
Robotic Hysterectomy
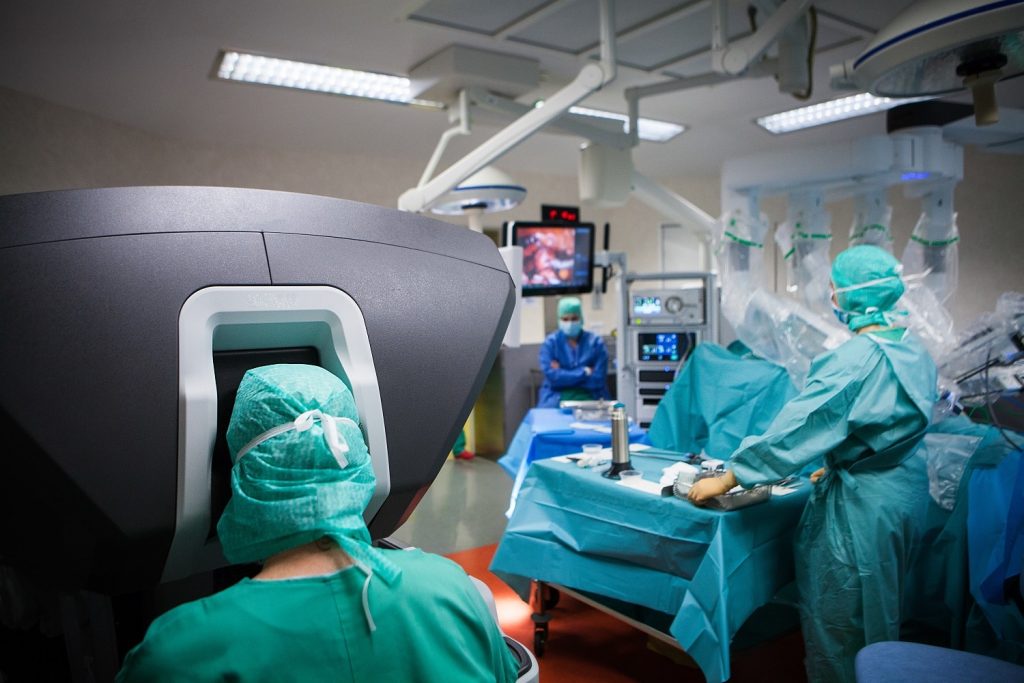
Robotic hysterectomy uses advanced robotic technology to perform the removal of the uterus with precision and control beyond traditional surgical techniques. At Alexandria Women’s Center, we utilize a state-of-the-art robotic surgical system, which features robotic arms controlled by the surgeon from a console. This system provides enhanced visualization, increased precision, and improved access to the surgical site.
Advantages of Robotic Hysterectomy
Robotic technology brings several key benefits to gynecological surgery, including:Enhanced Precision: The robotic system offers superior precision and control, allowing surgeons to perform delicate maneuvers that may be difficult with conventional techniques.Better Visualization: High-definition, 3D imaging provides surgeons with a clear view of the operating area, leading to more accurate surgery.Minimized Trauma: The minimally invasive nature of robotic surgery typically results in less tissue damage.Reduced Pain and Scarring: Smaller incisions mean less post-operative pain and smaller scars compared to traditional open surgery.Shorter Recovery Time: Patients often experience quicker recoveries and shorter hospital stays.Decreased Risk of Infection: Smaller incisions reduce the exposure of internal organs to potential external contaminants, decreasing the risk of postoperative infections.
Indications for Robotic Hysterectomy
Robotic hysterectomy is not suitable for everyone but may be recommended for patients with:Complex gynecological conditions such as extensive endometriosis or pelvic adhesive disease.Obesity or anatomical issues, where traditional laparoscopy is not feasible.Need for precision in difficult-to-access areas of the pelvis.
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, robotic hysterectomy carries potential risks, including:InfectionBleedingInjury to surrounding organs such as the bladder or intestinesComplications from anesthesiaIt is essential to discuss these risks with your doctor to determine if the benefits outweigh the potential complications in your specific case.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery from a robotic hysterectomy is generally faster than from an open surgical procedure, but it still requires careful postoperative care:Activity: Patients are usually encouraged to walk as soon as they are able after surgery to help prevent blood clots.Pain Management: Pain is typically less severe than with traditional surgery, but prescription pain relief may still be necessary.Follow-Up Appointments: Follow-up visits are crucial to monitor healing and manage any complications.Robotic hysterectomy represents a significant advance in surgical technology, offering numerous potential benefits over traditional surgical approaches. At Alexandria Women’s Center, we are committed to providing the latest in surgical technology and patient care. If you are considering a hysterectomy, ask your doctor if a robotic procedure could be an appropriate option for you.
Urinary Incontinence Surgery
Urinary incontinence is a common condition that affects millions of women, leading to the involuntary leakage of urine. This condition can significantly impact the quality of life but is often treatable through various methods, including surgery.
Types of Urinary Incontinence
There are several types of urinary incontinence, each with distinct causes and treatments:Stress Incontinence: Leakage occurs when pressure is exerted on the bladder by coughing, sneezing, laughing, or exercising.Urge Incontinence: Also known as overactive bladder, this involves a sudden, intense urge to urinate followed by an involuntary loss of urine.Mixed Incontinence: A combination of stress and urge incontinence.
Diagnostic Process
At Alexandria Women’s Center, our approach to diagnosing urinary incontinence includes:Medical History: Discussing symptoms, lifestyle, and any medical conditions that might affect bladder function.Physical Examination: Assessing the physical state of the urinary tract and surrounding areas.Bladder Tests: May include urodynamic testing to measure the pressure and volume of urine in the bladder.Imaging: Utilizing ultrasound or other imaging techniques to visualize the bladder and surrounding structures.
Surgical Treatments for Urinary Incontinence
Depending on the type and severity of incontinence, several surgical options may be considered:Sling Procedures: The most common surgery for stress incontinence, involving the placement of a synthetic mesh or natural tissue sling around the neck of the bladder to support it and prevent leakage.Bladder Neck Suspension: Aims to provide support to the urethra and bladder neck, typically used in cases where the sling procedure is not suitable.Injection of Bulking Agents: Involves the injection of synthetic materials around the urethra to help keep it closed and reduce leakage.Sacral Neuromodulation: Involves the implantation of a device that stimulates nerves to control bladder function, used primarily for urge incontinence.Botox Injections: Used for urge incontinence, Botox can be injected into the bladder muscle, helping to relax it and reduce symptoms.
Benefits and Risks of Surgery
Surgical interventions for urinary incontinence can greatly improve a patient’s quality of life by reducing or eliminating symptoms. However, as with any surgery, there are potential risks:Surgical risks such as infections, bleeding, and adverse reactions to anesthesia.Post-surgical issues including temporary urinary retention or continued incontinence, which may require further treatment.
Making the Decision
Choosing the right surgical option involves a thorough discussion with your doctor about the expected outcomes, potential risks, and how surgery might affect your lifestyle. Our team at Alexandria Women’s Center is dedicated to providing personalized care, ensuring that all patients understand their options and receive the treatment that best suits their needs.Urinary incontinence, while challenging, is often manageable and treatable with the right interventions. Surgical options have evolved significantly, offering effective solutions to help regain control and improve overall well-being.


Pelvic Reconstruction Surgery
Pelvic reconstruction surgery is a specialized procedure designed to address various conditions that affect the pelvic floor—a network of muscles, ligaments, and tissues that support the organs in the pelvis. At Alexandria Women’s Center, our surgeons utilize the latest minimally invasive technologies and techniques to repair these structures, ensuring a quicker recovery with minimized discomfort.
Conditions Treated by Pelvic Reconstruction Surgery
Pelvic reconstruction surgery is often recommended for patients experiencing:Urinary Incontinence: Involuntary leakage of urine due to weakened pelvic muscles.Pelvic Organ Prolapse: Descending of pelvic organs into or out of the vaginal canal due to weakened support structures.Post-Hysterectomy Prolapse: Occurrence of pelvic organ prolapse after a hysterectomy.Bowel Problems: Issues such as constipation or fecal incontinence related to pelvic floor dysfunction.Overactive Bladder Syndrome: Urgency, frequency, and potentially incontinence that may be linked to pelvic floor issues.
Surgical Techniques and Approaches
Our experienced surgeons perform pelvic reconstruction using the following techniques:Absorbable Stitches: These are used to repair and tighten the pelvic floor muscles and ligaments, naturally absorbed by the body over time.Mesh Implantation: In cases where additional support is needed, a synthetic mesh may be used to reinforce the pelvic floor. The use of mesh is carefully considered, weighing benefits against potential risks.Minimally Invasive Procedures: Using laparoscopic or robotic-assisted surgical techniques that involve smaller incisions, resulting in less pain and quicker recovery.
Benefits of Pelvic Reconstruction Surgery
Patients undergoing pelvic reconstruction surgery can expect several potential benefits:Improved Organ Function: Correction of organ prolapse and alignment which can improve urinary, bowel, and sexual function.Reduced Pain and Discomfort: Alleviation of symptoms associated with prolapse and other pelvic floor disorders.Enhanced Quality of Life: Many patients experience a significant improvement in quality of life with reduced symptoms affecting their daily activities.
Risks and Considerations
While pelvic reconstruction surgery is generally safe, there are potential risks involved:InfectionBleedingPain or discomfortMesh complications (if used), such as erosion or infectionRecurrence of prolapseIt is important to discuss these risks thoroughly with your healthcare provider.
Recovery Process
Recovery from pelvic reconstruction surgery varies depending on the specific procedures performed:Post-Operative Care: Patients typically receive detailed instructions on managing pain, preventing infection, and recognizing potential complications.Activity Restrictions: Avoiding strenuous activities and heavy lifting for several weeks is usually recommended.Follow-Up Visits: Regular check-ups help ensure that the recovery is progressing well, and any complications are addressed promptly.Pelvic reconstruction surgery at Alexandria Women’s Center represents a commitment to restoring pelvic health using advanced surgical techniques. Our goal is to provide effective solutions that allow our patients to return to a comfortable, active lifestyle.
Endometrial Ablations
Endometrial ablation is a minimally invasive procedure aimed at treating excessive menstrual bleeding by removing or destroying the lining of the uterus (endometrium). This treatment is typically considered when other less invasive treatments, such as medication, have not been effective.
How Endometrial Ablation Works
The procedure does not require incisions and is usually performed on an outpatient basis under local or general anesthesia. Various methods can be used to achieve the ablation:Radiofrequency: Uses heat to destroy the lining.Cryoablation: Freezes the endometrial tissue.Heated fluid: Utilizes hot saline to remove the lining.Microwave energy: Uses microwave energy to destroy the tissue.Electrosurgery: Conducted with an electric tool through a hysteroscope inserted into the uterus.
Who is a Good Candidate for Endometrial Ablation?
Endometrial ablation is best suited for women who:Suffer from chronic heavy menstrual bleeding that has not responded to other treatments.Wish to avoid a hysterectomy and the longer recovery associated with it.Do not plan to have children in the future, as pregnancy after ablation is rare and risky.
Benefits of Endometrial Ablation
Many women choose endometrial ablation for its benefits, which include:Quick Recovery: Most women return to normal activities within a few days.High Success Rate: Many patients report significantly lighter periods, and some stop having periods altogether.Non-Surgical: No incisions are involved, which reduces the risks associated with surgeries like hysterectomy.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While endometrial ablation is generally safe, it does carry some risks, such as:Infection and bleedingHeat or cold injury to nearby organsPiercing of the uterine wall with surgical instrumentsRare chances of fluid overloadIt’s important to discuss these risks with your healthcare provider.
What to Expect During Recovery
Recovery from endometrial ablation is relatively quick:Immediately After Procedure: You may experience some cramping, mild pain, and vaginal discharge that can be watery and mixed with blood.First Few Weeks: It’s important to monitor your body’s response and report any unusual symptoms to your doctor.Long-Term: Most women see a significant reduction in menstrual bleeding, but it’s important to remember that ablation is not a form of contraception, and reliable birth control is still necessary.Endometrial ablation offers a potentially life-changing option for women suffering from severe menstrual bleeding, providing relief with minimal downtime and risks. At Alexandria Women’s Center, our team is committed to providing advanced, compassionate care to help women regain control over their health and improve their quality of life.

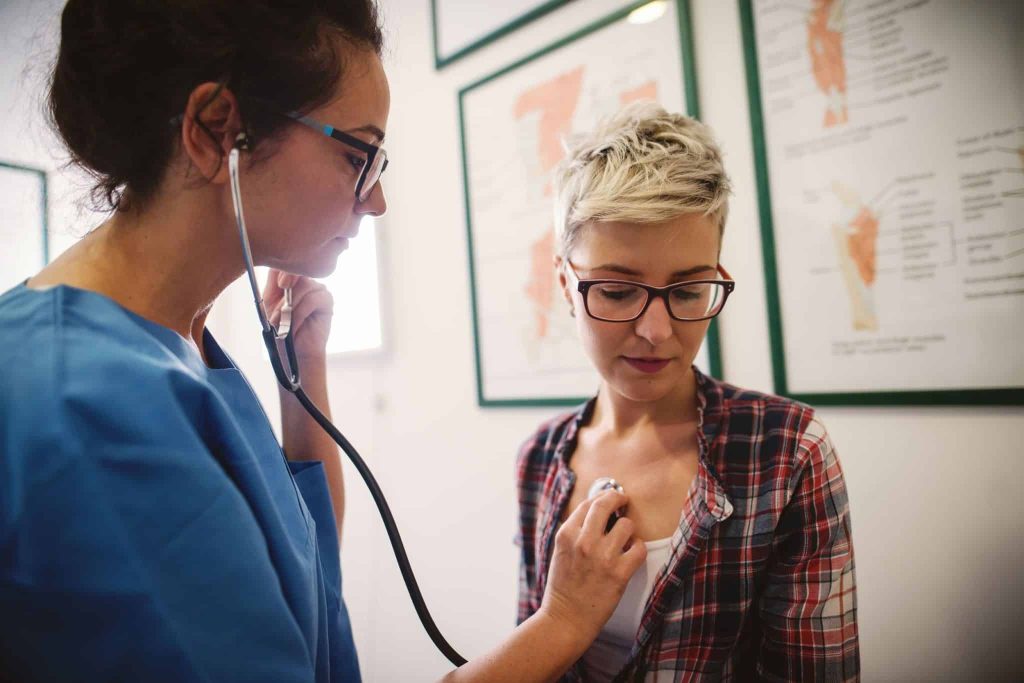
Myomectomy
A myomectomy is a surgical procedure specifically designed to remove uterine fibroids—noncancerous growths commonly found in the uterus during the childbearing years—while preserving the uterus. This procedure is often preferred by women who wish to retain their fertility or avoid a hysterectomy.
Types of Myomectomy
There are several types of myomectomy, each tailored to the size, location, and number of fibroids:Abdominal Myomectomy (Open Surgery): Ideal for large or deeply embedded fibroids, this method involves a larger incision in the lower abdomen to access and remove fibroids.Laparoscopic Myomectomy: Uses several small incisions in the abdomen to insert a camera and specialized instruments. This method is less invasive and typically offers quicker recovery and less scarring.Hysteroscopic Myomectomy: Performed through the vagina and cervix using a hysteroscope, this technique is suitable for fibroids that are inside the uterine cavity.
Why Choose Myomectomy?
Myomectomy is primarily chosen for the following reasons:Fertility Preservation: It is the preferred fibroid treatment for women who want to become pregnant or keep their uterus for other reasons.Symptom Relief: Effective in alleviating symptoms caused by fibroids, such as heavy menstrual bleeding, frequent urination, and pelvic pain.
Preparing for Myomectomy
Preparation for myomectomy typically involves:Preoperative Testing: Blood tests, imaging studies such as an ultrasound or MRI to map the fibroids, and a thorough pre-surgical assessment.Medications: Your doctor may prescribe drugs to reduce the size of fibroids before surgery.Fasting: As with most surgical procedures, you may be required to fast for a certain period before the surgery.
What to Expect During Surgery
The specifics of the procedure will depend on the type of myomectomy performed. General anesthesia is commonly used, so you will be asleep during the operation. The duration of the surgery can vary based on the number and size of the fibroids.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery from myomectomy can vary:Hospital Stay: From none (for hysteroscopic myomectomy) to several days (for abdominal myomectomy).Postoperative Care: Includes pain management and avoiding strenuous activities to allow proper healing.Follow-Up Visits: To check on healing and discuss further treatment or fertility planning if desired.
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any surgery, myomectomy carries risks such as:InfectionBleedingScar tissue formationRecurrence of fibroidsPossible challenges during future pregnancies, such as a need for cesarean delivery
Conclusion
Myomectomy offers a fertility-sparing option for women suffering from the discomfort and health issues caused by uterine fibroids. At Alexandria Women’s Center, we are committed to providing a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plans to help women maintain their reproductive health and improve their quality of life.

